Class 1: Transport in cells
During our last class, we studied how medicines travel through our body before reaching their target tissue or organ. Then, it is the job of the cell membrane to decide if the substances will enter the cell or not. This has a process that depends on the type of molecule that wants to enter the cell and the concentration of the substance both, outside and inside the cell.
The transport of molecules across the cell membrane
is a crucial process for the survival and function of
cells. The cell membrane, also known as the plasma
membrane, is a selectively permeable barrier that
controls the movement of substances in and out of
the cell. Transport across the cell membrane can occur
through various mechanisms that will be studied
in the next classes.
These processes play a key role in maintaining the balance of ions, nutrients, and other essential molecules within the cell and help cells to respond to changes in their environment.
After the introductory presentation, solve these activities to learn more about the first type of cell transport: DIFFUSION, also called SIMPLE DIFFUSION.
1. Watch the STUDY.COM video about diffusion
and explain with your own words how is the gas
exchange process related to this form of cell transport.
2. Explain what is diffusion (make sure you include the concentration levels). Then explain the metro example:
3. Visit the ThoughtCo. website, choose 4 examples of diffusion, draw them and explain them with your own words.
4. Visit the Byjus website and explain what is facilitated diffusion and draw the examples
Class 2: Osmosis
Osmosis is an essential process that occurs in living cells, it is the movement of water molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a semipermeable membrane, this means that it's like diffusion, but with water instead. In other words, it is the way water moves across cell membranes to maintain a balance between the concentration of water inside and outside the cell.
Today we will study some
examples of osmosis in different
living things and parts of the
body.
For example have you ever
wondered what can happen to
a fish from the sea in a river?
or the other way around?
1. Watch the Dr. Binocs video about osmosis and as you do it, answer these questions:
a) How does water move in osmosis?
b) Draw an area of higher and one of lower water concentration and explain the difference
c) Explain what happens to a fish from the sea when placed in freshwater.
d) What organ of the body works especially thanks to osmosis? what is its job?
2. There is an experiment that shows in a really simple way how osmosis works. Watch the video: experiment of osmosis in potato strips.
a) Explain the experiment with your own words
b) Why did some strips get bigger, and why did others shrink?
c) How does the water move in each case?
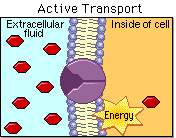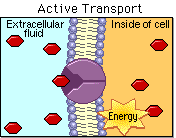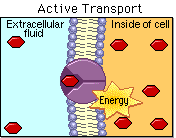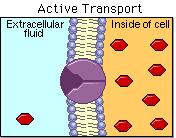
Class 3: Active Transport
Active transport helps our cells to do their job properly. Just like how we need food and water to survive, cells need nutrients and oxygen to function.
Active transport is like a superpower that enables cells to bring these important things inside, even if they are not naturally flowing in that direction. It's like walking up a hill instead of down! This process uses a lot of energy, which cells get from a special molecule called ATP. So, active transport is a very important process that helps cells to be healthy and do their job!
Today we will learn what active transport is, we will analyze some examples and will compare it to passive transport.
1) Visit the CK 12 website and answer the question:
a) Why is it called "active" transport?, what is ATP?
b)What are pumps? and why are they called like this?
2) Active transport also includes the use of vesicles. One example of this is a process called exocytosis. Visit the Future learn website and explain what is it, then draw the example.
3) Go to the Byjus website and explain why do plants need active transport?








Introductory
presentation